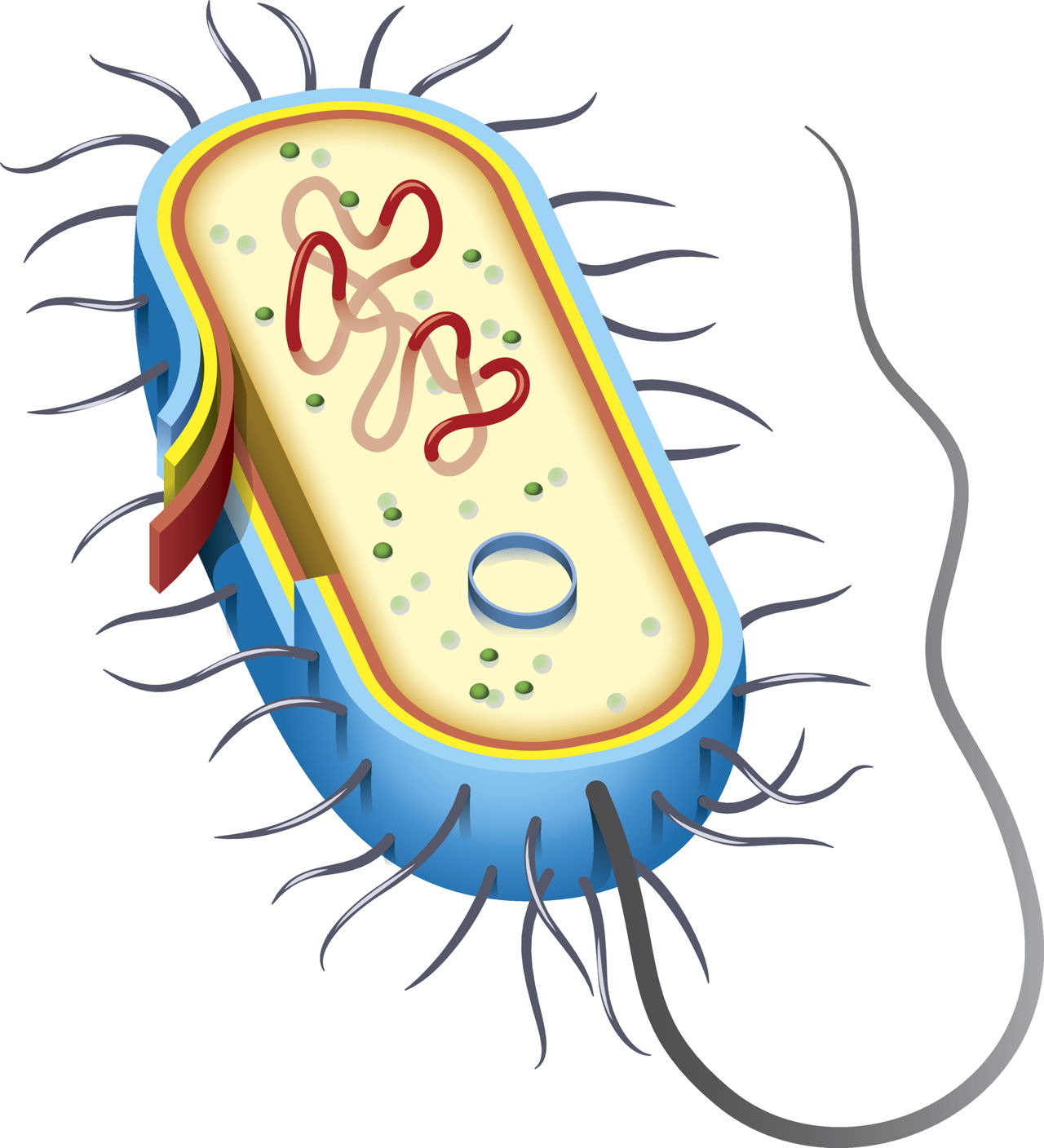
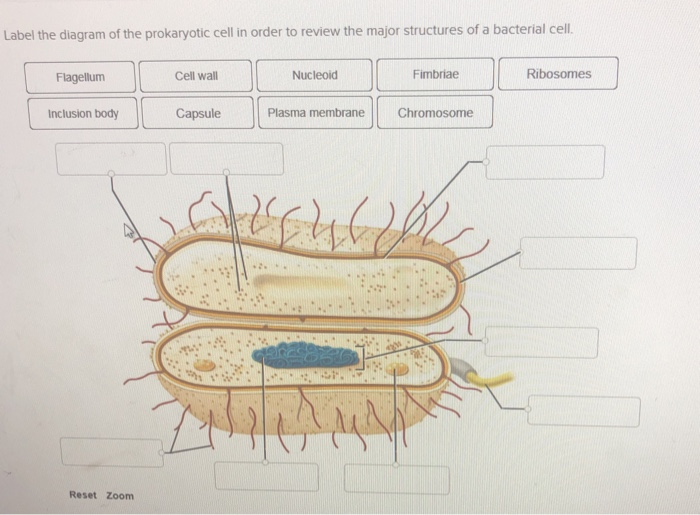
43 bacterial cell without labels
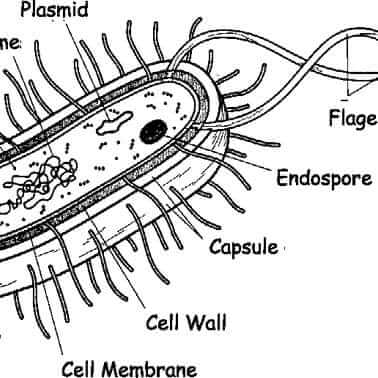
Components of Bacterial Cell: 7 Components (With Diagram) ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the seven important components of bacterial cell. The components are: 1. Cell Envelope 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleoid 4. Plasmids 5. Inclusion Bodies 6. Flagella 7. Pili and Fimbriae. Bacterial Cell: Component # 1. Cell Envelope: It is the outer covering of protoplasm of bacterial cell. Cell envelope consists of 3 […] Fast label-free identification of bacteria by synchronous fluorescence ... Bacterial cells consist of a very high amount of biological molecules whose content changes in response to different environmental conditions. The similarity between the molecular compositions of different bacterial cells limits the possibility to find unique markers to enable differentiation among species.
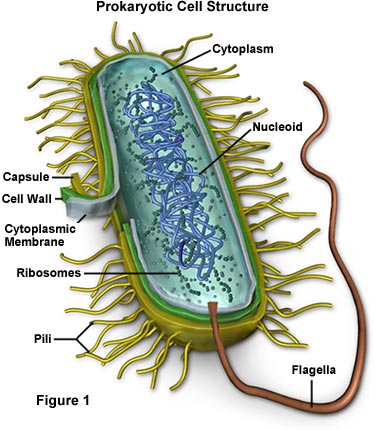
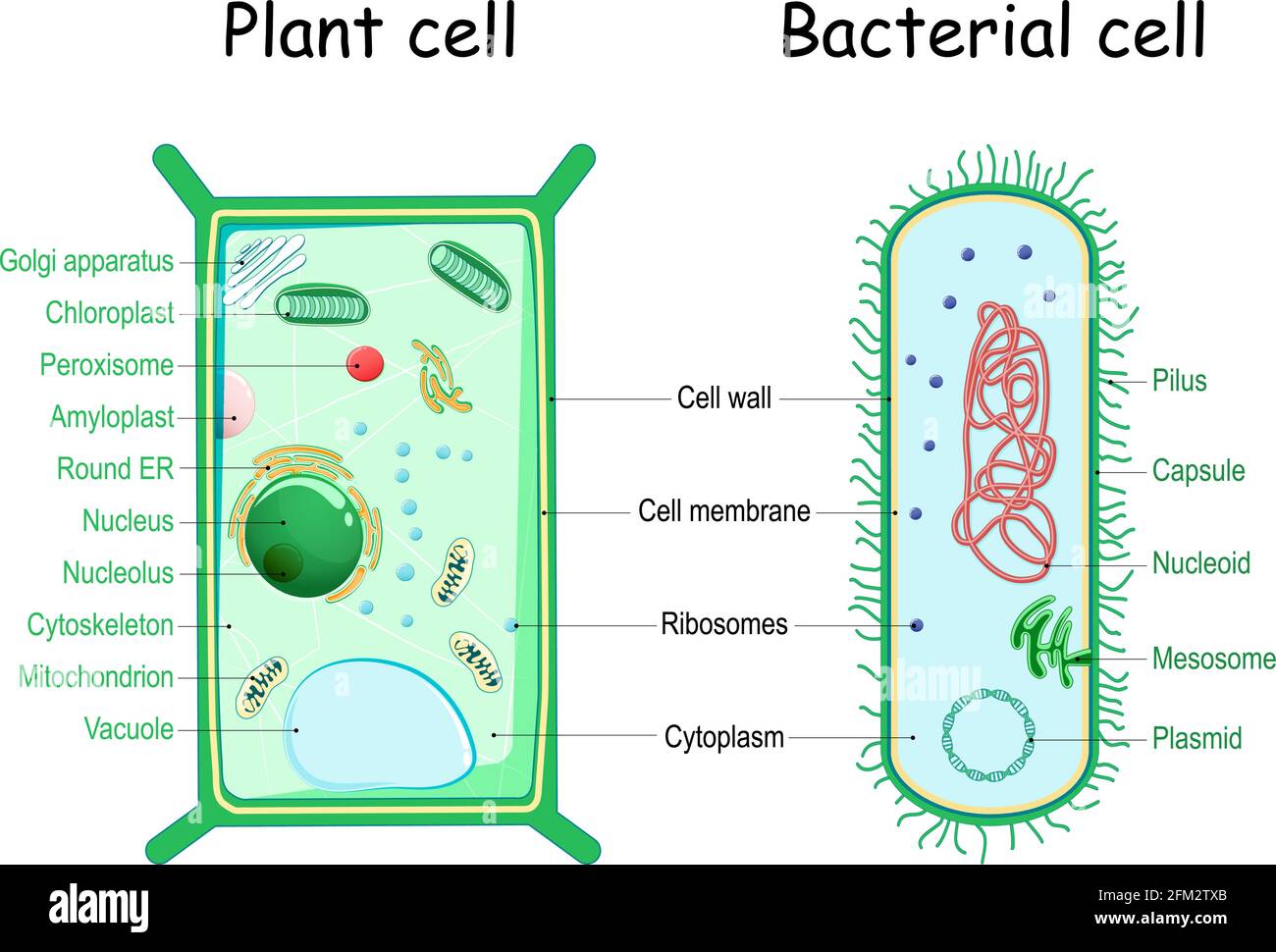
Bacterial cell structure and function - Online Biology Notes Bacterial are unicellular prokaryotic organism. Bacterial cell have simpler internal structure. It lacks all membrane bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, lysosome, golgi, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast, peroxisome, glyoxysome, and true vacuole. Bacteria also lacks true membrane bound nucleus and nucleolus.

Bacterial cell without labels
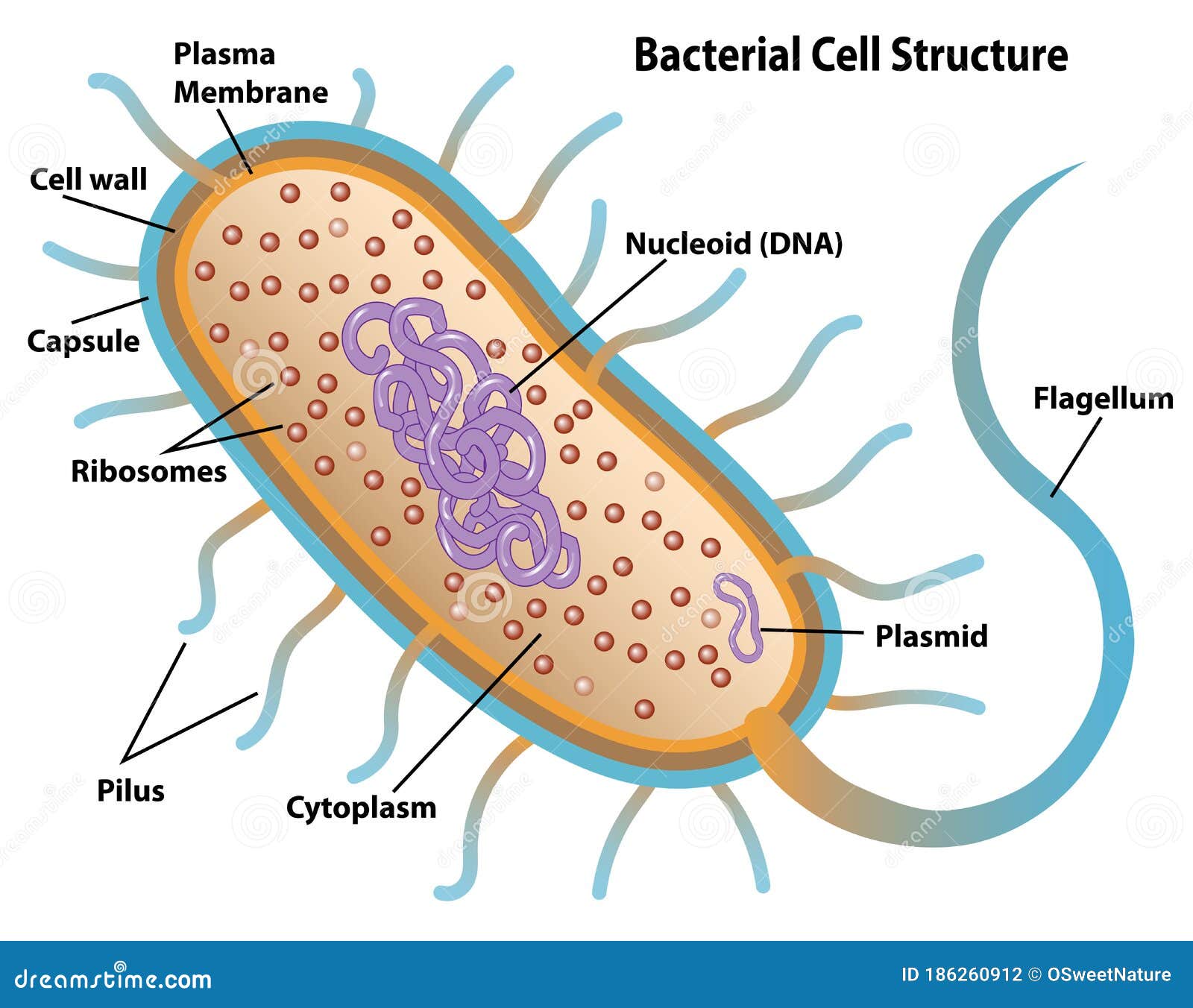
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology: Bacteria Cell Structure In gram-negative bacteria, the cell wall is thin and releases the dye readily when washed with an alcohol or acetone solution. Cytoplasm - The cytoplasm, or protoplasm, of bacterial cells is where the functions for cell growth, metabolism, and replication are carried out. It is a gel-like matrix composed of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes ... The Bacterial Cell Envelope - PMC - PubMed Central (PMC) Accordingly, E. coli and other enteric bacteria must have a cell envelope that is particularly effective at excluding detergents such as bile salts. This need not be a pressing issue for other Gram-negative bacteria, and their envelopes may differ in species- and environmentally specific ways. Morphology, Different shapes of bacterial cell - BYJUS These are non-motile, aerobic and gram-positive bacteria that cause many diseases.Examples of streptococci are Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus bovis, Streptococcus agalactiae, etc. Tetrads: Tetrads are arranged in a group of 4 cells.
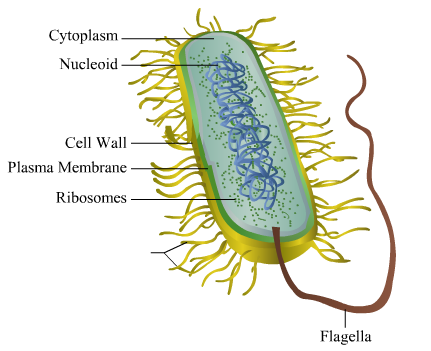
Bacterial cell without labels. Bacterial Cell: Structure and Components | Microbiology Bacterial cells (prokaryotic cells) are structurally much simpler than eukaryotic cells and the two cell types are compared in Table 3.2. They consists of various cell surface structures, cell wall, plasma membrane, many cytoplasmic inclusions, and the bacterial chromosome (nucleoid). Except some, all structures do not occur in every genus. Label or Concept - What Is a Pathobiont? - Trends in Microbiology The term ´pathobiont´ has already been widely used to label bacteria that have been linked to a disease merely based on sequence-based correlations with diseased individuals [. 23. ]. This is inherently error-prone as microbial community shifts can also occur as a consequence of disease [. 24. Structure - Medical Microbiology - NCBI Bookshelf Wall-Less Forms: Two groups of bacteria devoid of cell wall peptidoglycans are the Mycoplasma species, which possess a surface membrane structure, and the L-forms that arise from either Gram-positive or Gram-negative bacterial cells that have lost their ability to produce the peptidoglycan structures. Cytoplasmic Structures Bacteria in Microbiology - shapes, structure and diagram - Jotscroll Bacteria cells are the smallest living cells that are known; even though viruses are smaller than bacteria, viruses are not living cells. In microbiologythere are different types of bacteria with various sizes, shapes, and structures. The bacteria shapes, structure, and labeled diagrams are discussed below. Table of Contents Sizes Bacteria Shapes
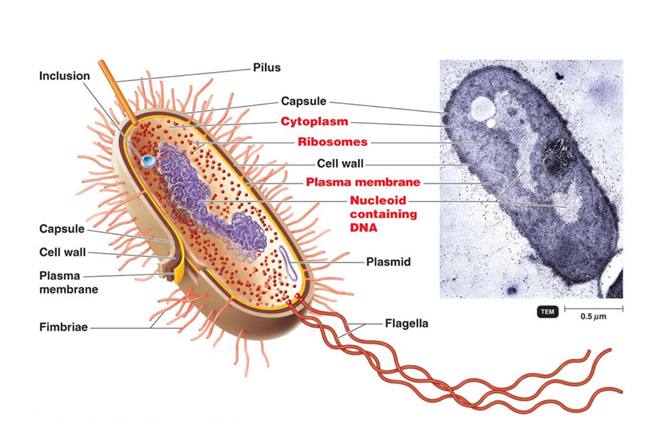
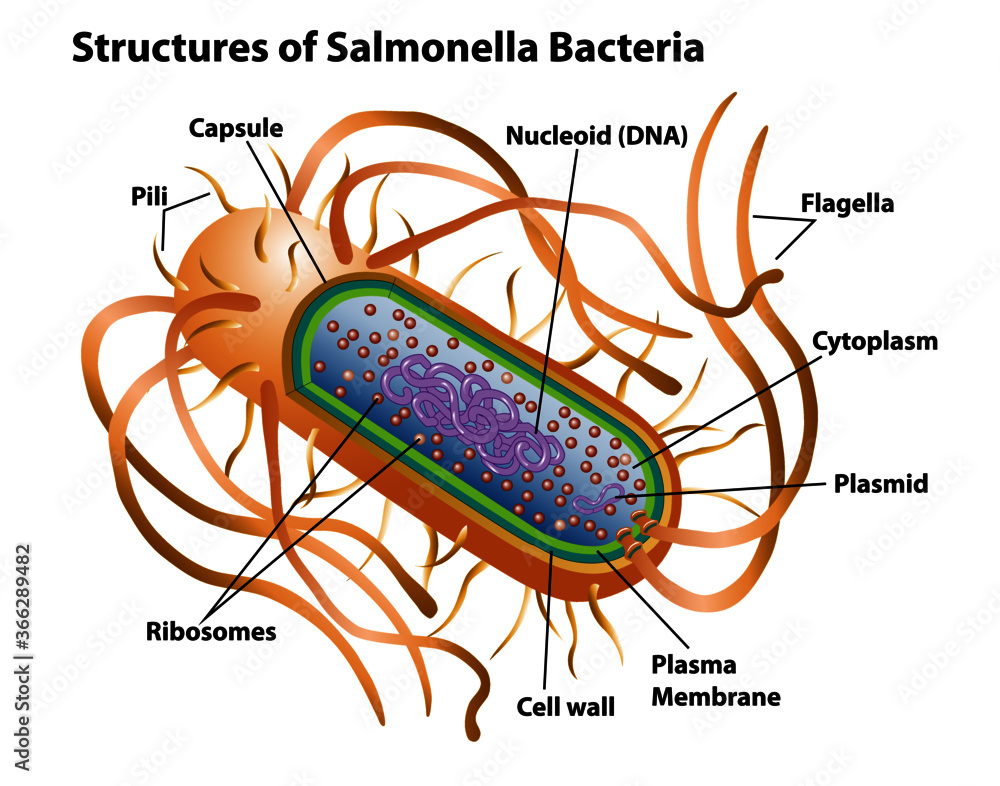
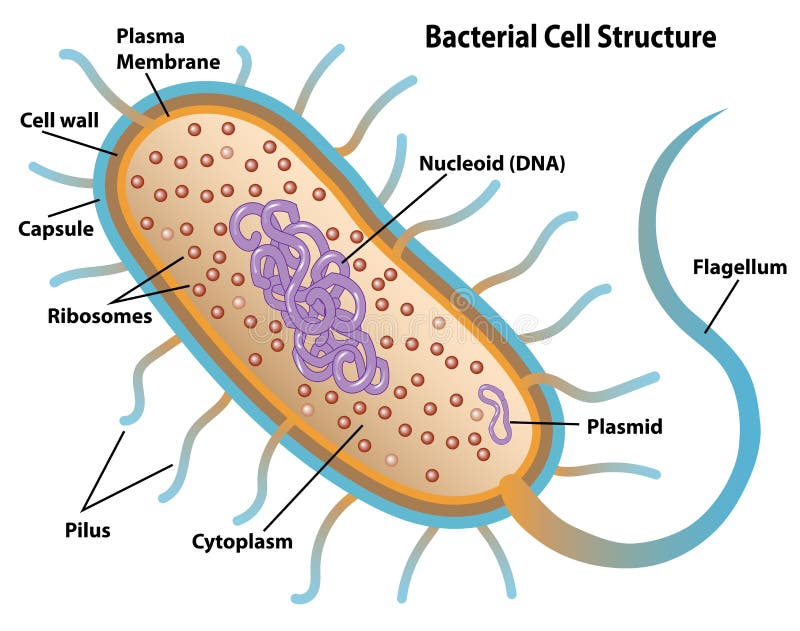
Bacterial cells with labels. - Healthclinic Bacterial cells with labels. The spheroid or ovoid or coccus. Bacillus. Vibrio. Spirillum. Spirochaete. Bacterial cells with labels. Bacteria cell anatomy Bacterial cells are microscopic unicellular organisms. The unit of measurement of bacteria is the micrometer (μm) and it is 1/1000 of a millimeter (.001μm). Stains - Microbiology Resource Center - Truckee Meadows ... - TMCC Almost all bacteria can be divided into two groups, Gram negative or Gram positive. A few bacteria are gram variable. Trichomonas, Strongyloides, some fungi, and some protozoa cysts also have a Gram reaction. Very small bacteria or bacteria without a cell wall, such as Treponema, Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, or Rickettsia do not have a gram reaction ... Bacterial Identification| 8 Methods & Tests In Microbiology - Study Read Identification by morphology: This method is to determine the individual bacterial physical appearance. 1. Based on size. Here bacteria are identified based on their physical size. Like small size or big one expressed in microns. For this bacteria are viewed under a microscope to view the size. Structure and Function of a Typical Bacterial Cell with Diagram A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell. The cell structure of a bacterial cell consists of a complex membrane and membrane-bound protoplast. There are also cell walls, cytoplasm, and nucleoids (genetic material) are present in the bacterial cell. The different parts of a typical bacterial cell are described below:
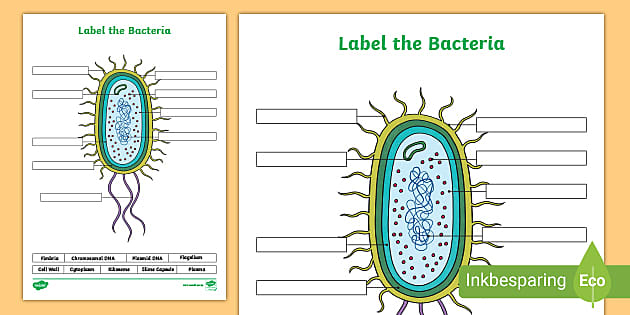
Shapes of Bacteria | Bacteria Shapes and Arrangements | Biology Explorer Bacteria or a bacterium (sing.) are simple single-celled organisms that lack organized nucleus and any chlorophyll pigments but they possess a rigid cell wall. The rigidity of its cell wall determines the shape of a bacterium. It also endows the bacterium with flexibility and other added advantages. Bacteria Label Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers Plant Cell, Animal Cell, Bacteria Cell Structure Science Poster Labels Anatomy. by. Mrs Wonder's Classroom. $10.00. Zip. Bright colorful set of 3 science printable posters. Plant, Animal and Bacteria cell structure with labels to be used as educational art for any kid's playroom, classroom, Montessori or homeschooling areas.Science Printable ... Introduction to Bacteria | Let's Talk Science Bacterial cells are much smaller than human cells. Bacterial cells can measure from about 1 to 10 μm long. Most of them are only about 1 to 2 μm in diameter. 1 μm, or micrometre, is 1 000 times smaller than a millimetre. That is very tiny! It's much smaller than the human red blood cell, which is (on average) about 7 μm in diameter. Bacterial cells - Cell structure - Edexcel - GCSE Combined Science ... Bacterial cells Bacteria are all single-celled. The cells are all prokaryotic. This means they do not have a nucleus or any other structures which are surrounded by membranes. Larger bacterial...
Gram-negative bacteria- cell wall, examples, diseases, antibiotics The cell wall of gram-negative bacteria is complex having a thin layer of the peptidoglycan layer of 2-7nm and a thick outer membrane of 7-8nm thick. Microscopically, there is a space that is seen between the cell membrane and the cell wall, known as the periplasmic space made up of periplasm. However it is found in both Gram-negative and Gram ...
Bacteria - Definition, Structure, Diagram, Classification - BYJUS The structure of bacteria is known for its simple body design. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles; hence, they are classified as prokaryotic organisms. They are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions. Such organisms are called extremophiles.
Label-free bacterial imaging with deep-UV-laser-induced native ... We also demonstrate the first noninvasive detection of bacteria on in situ-incubated environmental experimental samples from the deep ocean (Lo'ihi Seamount), showing the use of DUV native fluorescence for in situ detection in the deep biosphere and other nutrient-limited environments. Publication types Research Support, U.S. Gov't, Non-P.H.S.
Bacteria Under the Microscope Mix the bacteria on the loop with the water you placed on the glass slide earlier and then flame your loop once again. Finally, allow the slide to air dry. Staining Procedure When looking at bacteria under the microscope much of the bacteria can appear transparent without staining. Staining allows different structural components of the cells to ...
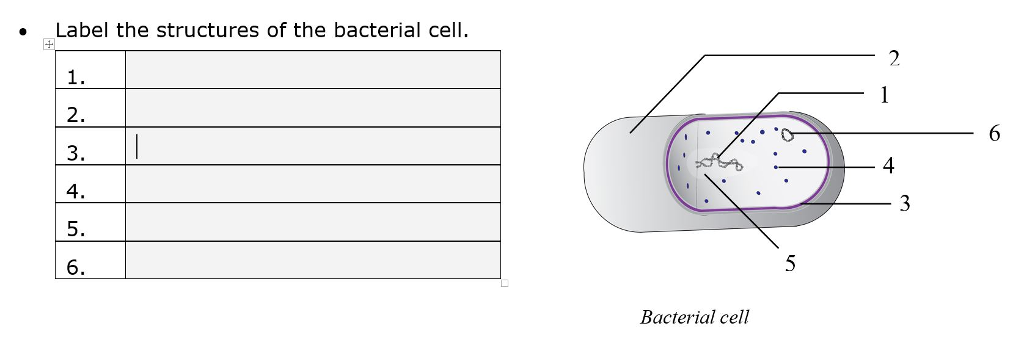
Bacterial Cell Structure Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Cytoplasm Water-based solution filling the entire cell Ribosomes Tiny particles composed of protein and RNA that are the sites of protein synthesis Nucleoid Composed of condensed DNA molecules. Cell Membrane A thin sheet of lipid and protein that surrounds the cytoplasm and controls the flow of materials in and out of the cell S Layer
3 Common Bacteria Shapes - ThoughtCo Spirochetes (also spelled spirochaete) bacteria are long, tightly coiled, spiral-shaped cells. They are more flexible than spirilla bacteria. Examples of spirochetes bacteria include Borrelia burgdorferi, which causes Lyme disease and Treponema pallidum, which causes syphilis. Vibrio Bacteria
Different Size, Shape and Arrangement of Bacterial Cells Bacilli (or bacillus for a single cell) are rod-shaped bacteria. Spirilla (or spirillum for a single cell) are curved bacteria which can range from a gently curved shape to a corkscrew-like spiral. Many spirilla are rigid and capable of movement. A special group of spirilla known as spirochetes are long, slender, and flexible. Arrangement of Cocci
Phases of the Bacterial Growth Curve - ThoughtCo Bacterial cell growth reaches a plateau, or stationary phase, where the number of dividing cells equal the number of dying cells. This results in no overall population growth. Under the less favorable conditions, competition for nutrients increases and the cells become less metabolically active.
Breaking free of labels | Nature Reviews Microbiology Talà et al. took steps to minimize the phototoxicity of iSCAT to the bacterial cells by employing a relatively low energy (638 nm) laser that was shuttered to reduce the cell exposure.
Interactive Bacteria Cell Model - CELLS alive Mycoplasma are bacteria that have no cell wall and therefore have no definite shape. Outer Membrane: This lipid bilayer is found in Gram negative bacteria and is the location of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in these bacteria. Gram positive bacteria lack this layer. LPS can be toxic to a host and can stimulate the host's immune system.
Bacteriophage - Wikipedia A bacteriophage (/ b æ k ˈ t ɪər i oʊ f eɪ dʒ /), also known informally as a phage (/ ˈ f eɪ dʒ /), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea.The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν (phagein), meaning "to devour".Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that ...
Morphology, Different shapes of bacterial cell - BYJUS These are non-motile, aerobic and gram-positive bacteria that cause many diseases.Examples of streptococci are Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus bovis, Streptococcus agalactiae, etc. Tetrads: Tetrads are arranged in a group of 4 cells.
The Bacterial Cell Envelope - PMC - PubMed Central (PMC) Accordingly, E. coli and other enteric bacteria must have a cell envelope that is particularly effective at excluding detergents such as bile salts. This need not be a pressing issue for other Gram-negative bacteria, and their envelopes may differ in species- and environmentally specific ways.
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology: Bacteria Cell Structure In gram-negative bacteria, the cell wall is thin and releases the dye readily when washed with an alcohol or acetone solution. Cytoplasm - The cytoplasm, or protoplasm, of bacterial cells is where the functions for cell growth, metabolism, and replication are carried out. It is a gel-like matrix composed of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes ...




















Post a Comment for "43 bacterial cell without labels"